In Windows, the two main command-line interfaces are Command Prompt (CMD) and PowerShell. Microsoft’s Windows Command Reference provides an A-Z guide with syntax, examples, and overviews of most commands.
CMD
The Command Prompt (cmd.exe) executes commands. Access it via Start Menu, Run dialog (cmd), or directly from C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe.
PowerShell
PowerShell is a Windows scripting language for automation and system management. Built on .NET Framework, it provides powerful tools for controlling and configuring Windows environments.
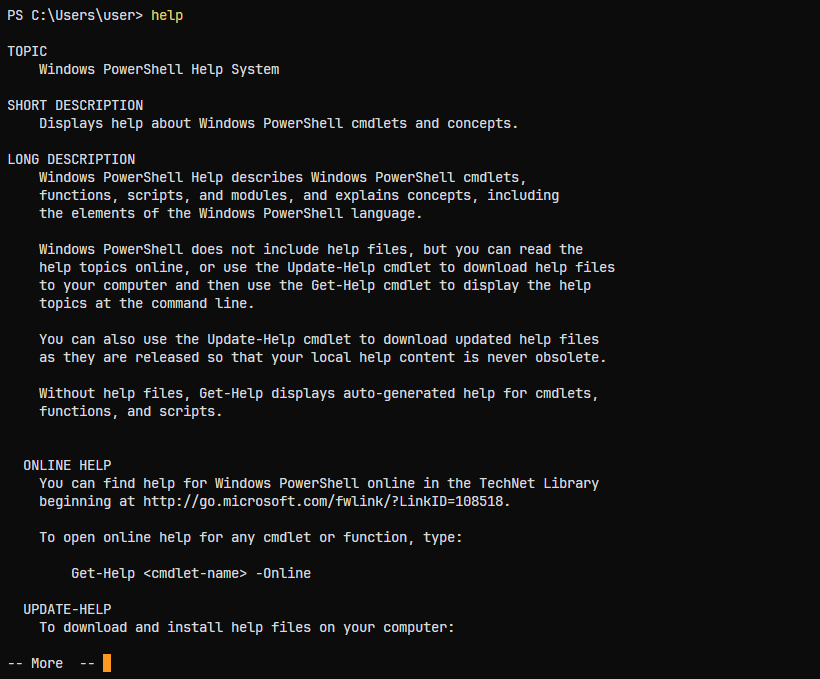
Execution Policy
Sometimes script execution is blocked by the PowerShell execution policy, a security feature that prevents potentially malicious scripts.
The available policy settings include:
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
AllSigned | All scripts must be signed by a trusted publisher. Prompts before running scripts from untrusted publishers. |
Bypass | No blocking of scripts or configuration files. No warnings or prompts. |
Default | Sets default policy: Restricted for Windows desktops, RemoteSigned for Windows servers. |
RemoteSigned | Requires digital signatures only for scripts downloaded from the internet. Local scripts run without signatures. |
Restricted | Allows individual commands but blocks script execution. Blocks all script files (.ps1xml, .psm1, .ps1). |
Undefined | No policy set for current scope. If all scopes are undefined, defaults to Restricted. |
Unrestricted | Default for non-Windows computers. Allows unsigned scripts with a warning for non-local intranet scripts. |
Bypass